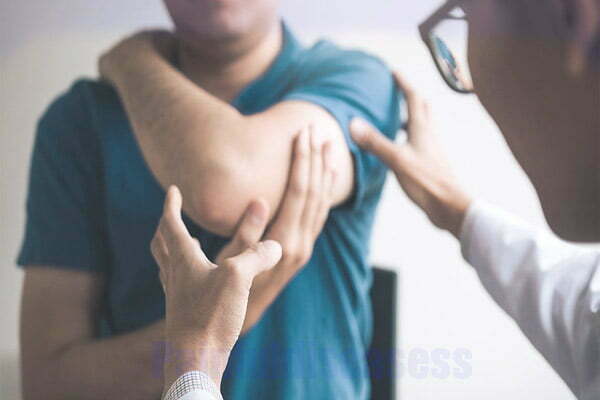
Wrist and elbow pain. The elbow pain we experience is often caused by wrist movements. The most common diseases in the elbow are pain due to strains at the attachment points of the tendons. These depend more on repetitive and forceful movements of the wrist. In addition, people with arthritic tendons often develop other arthritis-related pain, which can also be very uncomfortable.
Possible Causes of Wrist and Elbow Pain
We have found that over 25 percent of individuals with elbow problems actually have other arthritic pain disorders that can be associated with elbow pain. These people could also be at risk of developing pain due to osteoarthritis, a type of osteoarthritis that can be caused by repeated low-level trauma or chronic trauma such as a fracture, car accident, or an infection.
Osteoarthritis and other bone disorders of the elbow include acute arthrogryposis, which is a condition caused by an infection in the joint; tendonitis, a chronic, acute disease involving the tendons of the forearm and sometimes the elbow or arm; and tendonitis, a chronic condition that can be caused by a chronic low-level trauma or infection.
Arthrogryposis is the most common type of bone arthritis in the elbow; tendonitis is the most common type of bone arthritis in the elbow. Some patients with these arthritis types develop tendonitis and arthrogryposis together.
How are Injuries Sustained in Professional Sports and Other Activities?

In addition to arthrogryposis and tendonitis, some injuries sustained during sports activities may also cause pain and swelling.
These include:
- A sprained or broken bone.
- A sports injury which involves the wrist, elbow, or elbow and shoulder.
- A sports injury sustained while jumping, leaping, swinging, skiing, or skating.
- An amputation, sometimes known as a contusion, due to a sports injury.
- A sprained muscle due to an injury sustained during a contact sport.
An injury sustained in a noncontact sport that causes swelling at the site of the injury.
Arthritis Symptoms
Pain on an arm, elbow, or other limb often indicates that your pain is a result of arthritis. Pain usually affects the wrist and is often accompanied by stiffness and swelling of the muscles in the area of the pain. Pain in your elbow or wrist often indicates that it is an arthrogryposis injury or that you have some type of other arthritis.
Treatment for Arthritis
When you see a doctor for symptoms such as arthritis pain, an orthopedist should do an assessment of the condition. Depending on the severity of the pain, an experienced orthopedist may provide surgery. Osteoarthritis in the elbow can be treated successfully, although an experienced orthopedist will also recommend a specific treatment strategy.
To help improve the treatment options for arthrogryposis, you should discuss this with your doctor. Your doctor might recommend:
A Prescription for Pain-relieving Medication for Arthritis Pain
A pain-relieving medication that relieves pain, like a narcotic narcotic (opioid), such as morphine or codeine. These medications can decrease symptoms associated with the osteoarthritis.
A muscle relaxant such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, naproxen, or meloxicam. This reduces inflammation and pain. However, acetaminophen and naproxen can increase your risk of complications from the arthritis.
A corticosteroid steroid. This can help the arthrogryposis.
- Migraine headaches
- Osteoarthritis in the joint (OAJ), particularly in the elbow.
- Low blood pressure
- Other illnesses
Other treatment options include:
Nerve blocking medication, called nerve blocks. This can reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation and reduce the possibility of complications from the arthritis.
Prognosis
Arthrogryposis in the elbow may require corrective surgery, although it is rare for arthrogryposis to progress to pain and a permanent degenerative arthritis. If your arthrogryposis develops into arthritis, you should always see your doctor to talk about the possibility of having this surgery.



