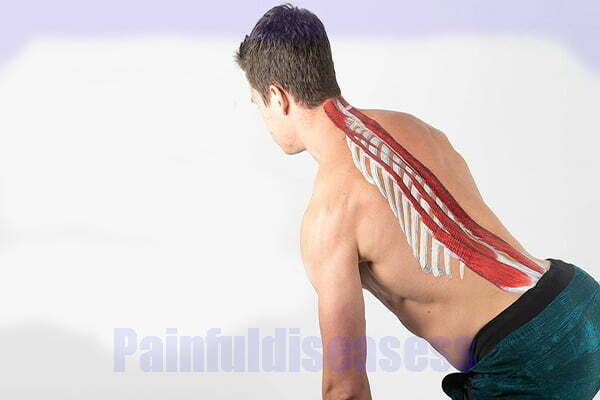
Erector spinae muscles pain. The erector spinae muscles are three muscles: spinalis, longissimus, and iliocostalis. The muscle group extending along the spine is the hidden cause of many pains such as back pain and headache.
If the erector spinae muscles are not injured, there may be temporary pain. Erector spinae muscle pain can have many causes. These may include:
Poor posture: If you have long hair it may seem like you’re trying to avoid your back. Don’t over-extend the back or sit straight and stiffly.
If you have long hair it may seem like you’re trying to avoid your back. Don’t over-extend the back or sit straight and stiffly.
When you’re not lying down, sitting in a chair or standing, your spine and neck might be more relaxed than usual. This leads to greater muscle tension and pain.
Injury: One common cause is an injury to the spinal nerves.
A person with a spinal stenosis may experience a lower back pain when sitting upright or kneeling. In such cases, the leg should be straight, and you should always be careful to keep your back straight.
Other causes: The causes for most pain in the back are not well-known. One of the best ways to investigate back pain is by your doctor. He may examine you and ask about your daily activities or history of back problems. Asking your doctor about your health is an important way to improve your chances of feeling better.
Preventing back pain
The best way to avoid back pain is to avoid over-extending the back. For a complete back rehabilitation, such as stretching or strengthening, take frequent breaks. Walking may also help. Also be sure to avoid lying on your back while you work or read.
Talk with your doctor. Discuss your back pain and other conditions with your doctor. He may have a more detailed medical history.
Take medication for pain. When possible, your doctor can recommend medicine that is more effective than others. Ask if he is prescribing drugs for your pain. You might also want to avoid taking prescribed drugs if possible.
When possible, your doctor can recommend medicine that is more effective than others. Ask if he is prescribing drugs for your pain. You might also want to avoid taking prescribed drugs if possible. Avoid excessive walking. For example, if you want to get to a meeting on time, find a quieter place.
Consider other ways of preventing back pain.
Take care of yourself
Try not to aggravate back pain or get more back pain.
Try not to aggravate back pain or get more back pain. Avoid lying down. While not as common as spinal stenosis or a back injury, it can happen when lying on your back, especially when lying flat on your back.
While not as common as spinal stenosis or a back injury, it can happen when lying on your back, especially when lying flat on your back. Use a lower back support. Your doctor might recommend a lower back support for a more effective back rehabilitation.



